… Activates National Multisectoral Emergency Operations Centre
Dr Ifedayo Adetifa, Director General of the Nigerian Centre for Disease Control (NCDC), has confirmed that 21 confirmed cases of monkeypox virus have been recorded from nine states and the Federal Capital Territory (FCT), with one death.
The states are: Adamawa (5), Lagos (4), Bayelsa (2), Delta (2), Cross River (2), FCT (2), Kano (2), Imo (1), Rivers (1) are among the states (1). The fatality was recorded in a 40-year-old patient who was on immunosuppressive drugs and had underlying co-morbidity.
The NCDC’s National Reference Laboratory in Abuja is doing genomic surveillance, and all of the cases have been verified to be caused by the West African clade Monkeypox virus so far.
Meanwhile, the Nigerian Center for Disease Control and Prevention (NCDC) has launched a national multisectoral Monkeypox Emergency Operations Centre (MPX-EOC) at level 2 to strengthen and coordinate ongoing response activities in-country while contributing to the global response.
This was based on the report of a preliminary risk assessment done by a group of Subject Matter Experts from the NCDC, relevant government Ministries Departments and Agencies and partner agencies.
This year, as at 29th May 2022,
Among the 21 cases reported in 2022 so far, there has been no evidence of any new or unusual transmission of the virus, nor changes in its clinical manifestation documented (including symptoms, profile and virulence).
Prior to the activation of the MPX-EOC, a multi-agency Technical Working Group (TWG) coordinated at the NCDC led Nigeria’s efforts to improve the detection, prevention and control of Monkeypox. Nigeria’s national surveillance system, the Surveillance Outbreak Response Management and Analysis System (SORMAS) was first deployed in response to the 2017 Monkeypox outbreak to improve the timeliness and completeness of case reporting, as well as facilitate the overall response (access relevant publication here – http://hdl.handle.net/10033/622144). In addition, this pilot project informed the nationwide scale-up of SORMAS to enable real-time reporting of surveillance data for prompt public health response to infectious disease outbreaks including COVID-19.
Following the detection of the index case on September 22, 2017 and the effective containment of the 2017 outbreak in Nigeria, the NCDC through the Monkeypox TWG worked on various interventions to gain a better understanding of the epidemiology of the virus to inform preparedness and response in-country (access NCDC-affiliated Monkeypox publications via https://ncdc.gov.ng/research).
The TWG coordinated the development of national Monkeypox guidelines, capacity building of healthcare workers and surveillance officers on case detection, sample collection, laboratory testing for confirmation and sequencing of the virus at NCDC’s National Reference Laboratory and intensified public awareness through risk communication. The national Monkeypox response guidelines can be accessed via – https://ncdc.gov.ng/themes/common/docs/protocols/96_1577798337.pdf.
Furthermore, a national One-health risk surveillance and information sharing (NOHRSIS) group has been inaugurated to facilitate timely information exchange on all prioritised zoonotic diseases. NOHRSIS will also strengthen the collaborative efforts of the One health/IHR Unit at the Point of Entry to intensify surveillance for the disease in animals as well as ensure minimal contact with suspected animals.
In addition, the One Health Animal Surveillance team including Federal Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development, Federal Ministry of Environment, National Veterinary Research Institute and partners commenced operational research on Monkeypox virus prevalence in small mammals at the human-animal interface since October 2018. This research has been completed in 7 states with a planned roll out in all other states to commence soon.
Although Nigeria’s risk of exposure to the Monkeypox virus is high based on the recent risk assessment conducted at NCDC, the current situation in-country and globally has shown no significant threat to life or the community that can result in severe disease or high case fatality rate. The EOC will continue to monitor the evolving situation to inform public health action accordingly.
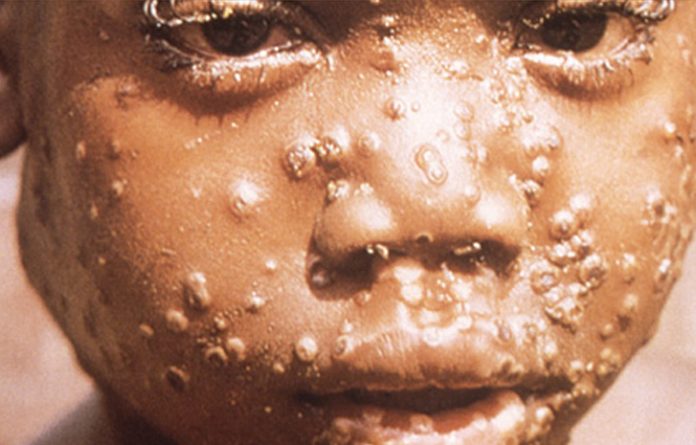
Symptoms of monkeypox include sudden fever, headache, body pain, weakness, sore throat, enlargement of glands (lymph nodes) in the neck and under the jaw, followed by the appearance of a rash (often solid or fluid-filled at the onset) on the face, palms, soles of the feet, genitals and other parts of the body. The Monkeypox public health advisory can be accessed via – https://ncdc.gov.ng/news/367/public-health-advisory-on-monkeypox.
The NCDC emphasises that members of the public should remain aware of the risk of Monkeypox and adhere to public health safety measures – specifically, report to the nearest health facility if you notice the known signs and symptoms of the disease. Healthcare workers are to maintain a high index of suspicion for Monkeypox and report any suspected case to the relevant state Epidemiology Team for prompt public health intervention including sampling for confirmatory testing.
About the NCDC
The Nigeria Centre for Disease Control is the country’s national public health institute, with the mandate to lead the preparedness, detection and response to infectious disease outbreaks and public health emergencies. The Bill for an Act to establish NCDC was signed into law in November 2018, by President Muhammadu Buhari. The mission for the NCDC (2017-2021) is ‘To protect the health of Nigerians through evidence-based prevention, integrated disease surveillance and response activities, using a One Health approach, guided by research and led by a skilled workforce’.